MTE 598
Addtiional
Constructions and Investigations
1. A ladder is leaning against a wall.
a) Pick an arbitrary point on the ladder and construct its locus as the ladder slides down the wall.
b) What curve does that point trace as the ladder slides along the wall?
2. Construct a sketch that goes with this situation:
A boy 5 ft tall walks away at a rate of 9 ft/sec from a street light 11 ft above ground. At what rate is the length of his shadow changing as he walks away from the light?
3. A rectangle is inscribed within a circle. Create a Sketchpad sketch that models this situation. (When you modify the rectangle its relation with the circle must remain invariant. Also, when you modify the circle, the rectangle must retain its relationship with the circle.)
4. Construct the locus of a point that forms an angle of fixed measure with the endpoints of a given segment.
Argue that the locus is what it appears to be. (Be careful not to beg the question!)
5. The following construction was created by Rene Descartes.
Let ÆKLM be any triangle, and let N be any point exterior to ÆKLM. Let P be the intersection of line KM and line NL.
a) What
type of curve appears to be made by the locus of point P as the triangle is
slid (intact) along the line containing ![]() ?
?
b) Argue in support of your claim in (a).
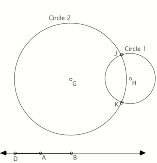
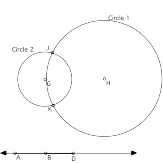
6. Three snapshots from a sketch are shown below. The sketch was made to create the locus of a point such that the difference of its distances from G and from H is constant.
Circle 2 has radius DB. Circle 1 has radius DA. As you move point D from the left of A to the right of B, the points of intersection of Circle 1 and Circle 2 (points J and K) trace a hyperbola.
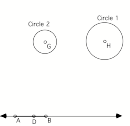
The above
narration assumes that the distance between G and H is greater than the
distance between A and B.
a) What
would be the locus of J and K if the distance between A and B is greater
than the distance between G and H? Why?
b) What
does all this say about the relationship between the two classes of curves
youÕve identified?
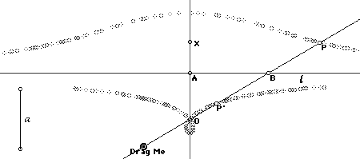
7. Let O be a fixed point on the line OX perpendicular at A to a fixed line l. Let any line through O meet l in B. On this line mark off BP=BP'=a. The locus of P (and P') is called a conchoid.